In this article, we will learn .NET Core Web API Data validation with FluentValidation.
What is Data Validation in Web API?
Data Validation simply tells the rules and validation that we apply to Data.
So, data Validation in Web API means, validating the data that is being sent by the client and if the data is not in the desired format then sending a message to the client about the error.
In order to understand the Data Validation in Web API, let’s create a model class named Product and add 3 properties as shown in below code snippet below.
public class Product
{
public string ProductCode { get; set; }
public int Stock { get; set; }
public string ProductName { get; set; }
}Now, we will create a ProductController class and add a Post method which accepts Product model as an input parameter.
Before posting the data to the server we need to check if all properties of the model class are in the correct format.
For example – The product Code field should not be blank, Stock must be greater than 0 (zero).
In the below code snippet, we are checking ProductCode and if it is blank or null then send a 400 (Bad Request) message to the client.
// POST api/<ProductController>
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Post(Product product)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(product.ProductCode))
{
return BadRequest();
}
return Ok();
}In case ProductCode is blank then the client will receive the below response.
{
"type": "https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1",
"title": "Bad Request",
"status": 400,
"traceId": "00-3738488015a04444b4f6f4b71938b168-591299b77d6d5344-00"
}However, the above response doesn’t describe the exact error details.
So, to show the exact error details, we will use ModelState as shown in below code snippet below.
// POST api/<ProductController>
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Post(Product product)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(product.ProductCode))
{
ModelState.AddModelError(nameof(product.ProductCode),
$"{nameof(product.ProductCode)} Can not be blank.");
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
return Ok();
}Now, the client will receive the below error message in case ProductCode is blank.
{
"ProductCode": [
"ProductCode Can not be null"
]
}What is FluentValidation in ASP.NET Core?
FluentValidation is one of the most famous .NET library to build validation rules. It provides extensive way to apply validations over model data. FluentValidation allows developer to define the validation rules in a clean and reusable fashion. It seamlessly work with .NET core based applications. Before moving further, let’s understand the complexity with traditional approach which defines why we need FluentValidation.
What is ModelState?
ModelState is a property available in the instance of a controller class. It is a collection of name and value pairs which are submitted to the server while doing a POST operation. It also contains error messages, if any.
So, in this way, if we have multiple properties to check then we need to write code as shown below.
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(product.ProductCode))
{
ModelState.AddModelError(nameof(product.ProductCode),
$"{nameof(product.ProductCode)} Can not be null");
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(product.ProductName))
{
ModelState.AddModelError(nameof(product.ProductName),
$"{nameof(product.ProductName)} Can not be null");
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (product.Stock <= 0)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(nameof(product.Stock),
$"{nameof(product.Stock)} Can not be 0");
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}But, this is a little bit lengthy and complex task.
Make it easy with FluentValidation
FluentValidation is a .NET framework-based library which helps to build strong type validation rules. It supports .NET Standard and .NET Core frameworks both.
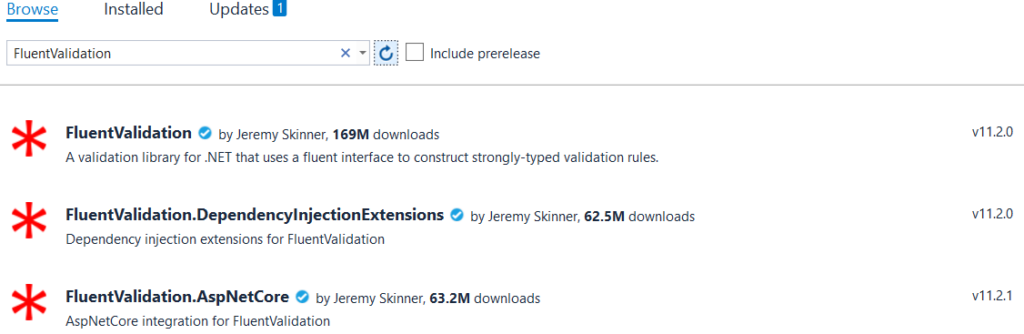
Install FluentValidation NuGet Packages
Firstly, we need to install the below packages from the NuGet package manager.
- FluentValidation
- FluentValidation.AspNetCore
- FluentValidation.DependencyInjectionExtensions
Code snippet for FluentValidation
So, to demonstrate this, first, create a class and inherit it from AbstractValidator<T>. Here T is the model class.
For this, we will use the below namespace.
using FluentValidation;public class ProductValidator : AbstractValidator<Product>
{
public ProductValidator()
{
RuleFor(x => x.ProductCode).NotEmpty();
RuleFor(x => x.ProductName).NotEmpty();
RuleFor(x => x.Stock).GreaterThan(0);
}
}Create the object of the Validator class and then use the ValidationResult class to fetch the result.
IsValid – Returns a boolean value which says if the validation has succeeded.
Now, we will write the below code in the Action method.
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Post(Product product)
{
ProductValidator validationRules = new ProductValidator();
ValidationResult validationResult = validationRules.Validate(product);
string message = "";
if (!validationResult.IsValid)
{
foreach (var failure in validationResult.Errors)
{
message = message + "Property " + failure.PropertyName + " failed validation. Error was: " + failure.ErrorMessage;
}
return BadRequest(message);
}
return Ok();
}You can return the error message in your way. So, by using FluentValidation we have minimised the code and achieved the validation status with built-in methods and rules.
Conclusion
So, in this article, we explored the data validation in Web API. To demonstrate the concept, I used FluentValidation which is a .NET framework-based library. This library helps us to easily apply validation rules on a member of a model class.