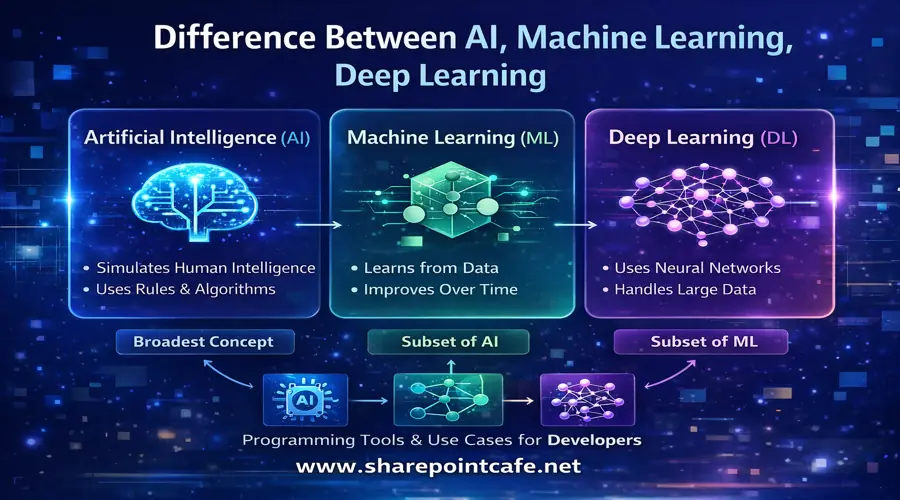
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are often used as interchangeable terms. However, they are not the same. Each concept builds on the previous one and plays a unique role in modern software development.
For programmers, understanding the difference between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning is essential. It helps in choosing the right tools, designing better applications, and building scalable intelligent systems.
This article explains these concepts in simple terms, with real-world examples, tools, use cases, and a practical C# .NET code snippet.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is the broadest concept. It refers to machines or software systems that mimic human intelligence to perform tasks such as reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, and language understanding.
AI systems follow predefined rules or logic and may or may not learn from data.
Key Characteristics of AI
- Works based on rules, logic, or algorithms
- Can be reactive or decision-based
- Does not always require learning from data
Examples of AI
- Rule-based chatbots
- Chess-playing programs
- Recommendation engines based on logic
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows systems to learn from data instead of being explicitly programmed. ML models improve their performance over time as they process more data.
In ML, programmers provide data and algorithms, and the system finds patterns automatically.
Key Characteristics of Machine Learning
- Learns from historical data
- Improves accuracy over time
- Requires data preprocessing and training
Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning (labeled data)
- Unsupervised Learning (unlabeled data)
- Reinforcement Learning (reward-based learning)
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain. It is especially powerful for handling large and complex datasets.
Deep Learning automatically extracts features from data without manual intervention.
Key Characteristics of Deep Learning
- Uses multi-layer neural networks
- Handles large volumes of data
- Requires high computing power
Examples of Deep Learning
- Image recognition
- Speech-to-text systems
- Self-driving car vision systems
Core Difference Between AI, ML, and DL
| Feature | AI | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad | Subset of AI | Subset of ML |
| Learning | Optional | Required | Required |
| Data Dependency | Low to Medium | Medium to High | Very High |
| Human Intervention | High | Medium | Low |
| Complexity | Low to Medium | Medium | Very High |
Popular Tools Programmers Use for AI, ML, and DL
1. TensorFlow
Official Website: https://www.tensorflow.org
How It Helps Programmers:
TensorFlow enables developers to build and train ML and DL models efficiently.
Use Cases:
- Image classification
- Predictive analytics
- Neural network training
2. PyTorch
Official Website: https://pytorch.org
How It Helps Programmers:
PyTorch provides flexibility and ease of use for deep learning research and production.
Use Cases:
- Computer vision
- Natural language processing
- AI research prototypes
3. Azure Machine Learning
Official Website: https://azure.microsoft.com/services/machine-learning
How It Helps Programmers:
Azure ML allows developers to build, train, deploy, and manage ML models using .NET and cloud services.
Use Cases:
- Enterprise AI applications
- Model deployment with APIs
- Integration with C# .NET
Real-World Use Cases
AI Use Cases
- Customer support chatbots
- Rule-based fraud detection
- Automated scheduling systems
Machine Learning Use Cases
- Sales forecasting
- Spam email detection
- Recommendation systems
Deep Learning Use Cases
- Facial recognition
- Speech recognition
- Medical image diagnosis
C# .NET Example: Simple Machine Learning Prediction
Below is a basic ML example using ML.NET in C#:
using Microsoft.ML;
using Microsoft.ML.Data;
public class HouseData
{
public float Size { get; set; }
public float Price { get; set; }
}
public class PricePrediction
{
[ColumnName("Score")]
public float PredictedPrice { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var context = new MLContext();
var data = new[]
{
new HouseData { Size = 800, Price = 100000 },
new HouseData { Size = 1000, Price = 130000 },
new HouseData { Size = 1200, Price = 160000 }
};
var trainData = context.Data.LoadFromEnumerable(data);
var pipeline = context.Transforms.Concatenate("Features", "Size")
.Append(context.Regression.Trainers.Sdca());
var model = pipeline.Fit(trainData);
var engine = context.Model.CreatePredictionEngine<HouseData, PricePrediction>(model);
var prediction = engine.Predict(new HouseData { Size = 1100 });
Console.WriteLine($"Predicted Price: {prediction.PredictedPrice}");
}
}
How AI Tools Help Here
- Generate boilerplate ML.NET code
- Explain regression logic
- Optimize feature selection
Which One Should Programmers Learn First?
- Beginners: Start with AI concepts
- Developers: Learn Machine Learning fundamentals
- Advanced Engineers: Move to Deep Learning
Understanding the hierarchy helps programmers choose the right approach for a problem.
FAQs – AI vs ML vs DL
Q1. Is Deep Learning better than Machine Learning?
Not always. DL is powerful but requires more data and resources. ML works better for smaller datasets.
Q2. Do I need math to learn AI?
Basic math helps, but modern tools abstract most complexity.
Q3. Can C# developers work with AI?
Yes. ML.NET and Azure ML support C# and .NET very well.
Q4. Is AI only for large companies?
No. Cloud platforms and open-source tools make AI accessible to everyone.
Q5. Which field has the highest demand?
Machine Learning and Deep Learning engineers are in high demand across industries.
Summary
AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are interconnected but distinct technologies. AI is the umbrella concept, ML enables systems to learn from data, and DL powers advanced intelligence using neural networks.
For programmers, understanding these differences is critical for building the right solutions. By choosing the correct tools and techniques, developers can create intelligent, scalable, and future-ready applications.
Keep Following: SharePointCafe.NET


Leave a Reply