Before ASP.Net Core 2.0 we had an MVC option to develop a web application. After the release of .Net Core 2.0, a developer has one more option to create a Web Application in .Net Core i.e. .Net Core Razor pages.
In this blog, we will see the differences between Web Applications (Razor Pages) and Web Applications (MVC) in ASP.Net Core. We will also see which type of Web Application is good for our project or requirement by looking at benefits and code comparison.
Recently I was creating a project in Visual Studio 2019/ 2022. I found 2 options in ASP.Net Core Web Application as below –
Web Application – A project template for creating an ASP.Net Core application with example ASP.Net Core Razor Pages content.
Web Application (Model-View-Controller) – A project template for creating an ASP.Net Core application with an example ASP.Net Core MVC View and Controllers. This template can also be used for RESTful HTTP services.
I scratched my head and was unable to decide which option I should select.
So, I decided to find out the core differences between these two so that we can easily figure out the differences between Razor Pages and MVC.
By the end of this article, you will see the pros and cons of these two also you will be able to differentiate between MVC and Razor Pages.
Razor Pages vs MVC
ASP.Net Core Razor Page is very similar to ASP.NET MVC’s view pages. It has a similarity in syntax and functionality to MVC. The major difference is that in an MVC application model, controller code is included or bonded with View pages.
Razor pages are the next evolution of traditional ASP.Net WebForms. MVC is good for those web application which has lots of dynamic server pages, REST APIs and AJAX calls.
For basic web pages and simple user input forms, we should go for Razor pages.
Razor pages are similar to ASP.Net web forms in the context of structure, except for page extension.
In ASP.Net web forms, we had .aspx for UI and .aspx.cs file for code behind, in ASP.Net Razor pages we have .cshtml for UI and .cshtml.cs for code behind.
So, we can say that Razor pages are more organized compared to MVC. In MVC lots of routing gets involved with the Model, Controller, and Actions within the Controller. But this is not the case with Razor pages.
We have a Razor view and code-behind file for this view to manage all actions and events on the View page.
Structure of Razor Pages and MVC
Razor pages do not have any kind of structure like MVC. All Razor pages reside under the Pages folder with a very basic structure. You may see the screenshot below. Further, you can organize your project structure based on your functionality.
The screenshot below will explain the differences between the project structure of .Net Core Razor pages and MVC.
Understand Razor pages vs MVC structure from the below image.
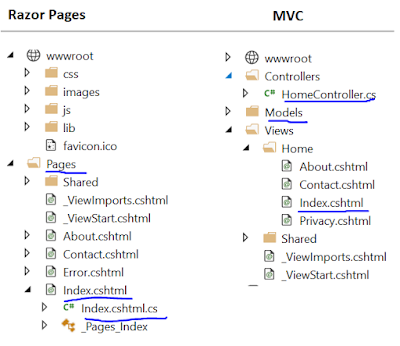
Razor Pages and MVC – Code Comparison
As we know, Razor pages and MVC look almost similar i.e. both having .cshtml as the file extension.
If we notice the 2 pages, one from Razor and another from MVC then we will notice @page at the top of Razor pages.
@page is a directive used in Razor pages.
Another difference is the model declaration in Razor pages.
In Razor pages model declaration is like
For index.cshtml – @model IndexModel
For about.cshtml – @model AboutModel
Adding a new Razor Page in the application
Right-click on the Pages folder in Solution Explorer and Select Add->Razor Pages
Select Razor Page from the below screen and click Add
Next, Give a name to the view and select the required options and click Add.
Default Code-behind for index.cshtml
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
public void OnGet()
{
}
}There is no code behind for MVC. In MVC, the developer has to use the controller file to create an Action method to link a particular View.
Page Routing
In Razor pages, default routing will find a Razor page from the Pages folder for a specific request. This means the routing configuration will try to find the same name in the Pages folder for which a request was generated.
So, if a user requests/home then routing will try to find a home in the pages folder.
However, this is not the case in MVC.
In MVC, the default routing configuration will try to find a matching controller and action to load a view.
Advantages of using Razor Pages
There are a few advantages of using Razor pages over MVC. Razor pages are easy to understand in the context of structure. They do not have a controller and action to load.
Razor pages contain code behind individual pages.
Conclusion
It is too early to analyze Razor pages as they are new. Razor pages are more structured and easy to understand compared to MVC. These pages are similar to traditional ASPX pages as Razor pages contain code-behind files too. Razor pages have a @page directive at the top of the page.
There could be lots of debate for deciding which one is better.
But, if you want to create a website with static pages or with a few dynamic pages, I think the Razor page is a good choice.
But If you are creating a REST-based API project or lots and lots of dynamic pages, you should go for MVC.
Enjoy learning Razor pages and MVC in ASP.Net Core.


Leave a Reply